Types of Hair Loss
THERE ARE 2 TYPES OF HAIR LOSS
1. GRADUAL HAIR LOSS
Commonly known as hormonal, progressive, or hereditary hair loss.
GRADUAL HAIR LOSS is generally caused by a reduced anagen phase (growth state) in the hair follicle. With ongoing gradual degeneration, each cycle becomes shorter than the one before it, and the process ends with the follicle wearing itself out completely.
To fight this type of hair loss, you must PROLONG THE LIFE OF THE ANAGEN PHASE.
2. SUDDEN HAIR LOSS
Also referred to as reactional hair loss.
SUDDEN HAIR LOSS is largely a result of many follicles entering the shedding (telogen) phase early.
To treat this type of hair loss, you need to QUICKLY REACTIVATE HAIR GROWTH by triggering a new hair cycle.
HOW TO IDENTIFY MY HAIR LOSS TYPE?
1. GRADUAL HAIR LOSS
SPAN: Usually noticeable after 6 months or more as hair thins out.
SCENE: Hair progressively loses thickness; some areas thin more than others.
TRIGGER: Often unknown or difficult to identify without professional help.
OTHER SYMPTOMS: Thinning hair with excess sebum (oily scalp) and a tight scalp.
2. SUDDEN HAIR LOSS
SPAN: Appears 2-3 months after a stressful event; hair seen on pillow, sink, etc.
SCENE: Hair loss is diffuse over the entire head, not in patches.
TRIGGER: Usually identifiable—examples include:
- Seasonal changes
- Stress or emotional shock
- Poor or restricted diet
- Fatigue, overexertion, illness
- Medical treatments
- Chemotherapy
LEARN MORE ABOUT HAIR LOSS TYPES
LEARN ABOUT THE HAIR GROWTH CYCLE
Our hair renews itself through three repeating phases.
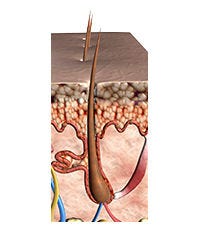
The Anagen Phase
Growth phase: 2-3 years (men), 6-8 years (women). About 85% of hair is in this stage.
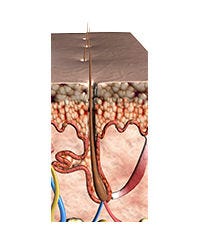
The Catagen Phase
Regression phase: 2-3 weeks. The follicle becomes inactive; hair stops growing but remains anchored.
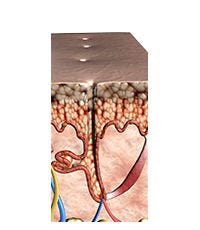
The Telogen Phase
Resting phase: lasts ≈ 3 months; the old hair sheds and a new anagen phase begins.
THE CAUSES OF HAIR LOSS
1. GRADUAL HAIR LOSS
POOR CIRCULATION
Insufficient micro-circulation deprives follicles of vitamins, oxygen, and amino acids.
HYPERSEBORRHEA
Excess testosterone causes over-production of sebum that worsens hair loss.
RIGID & INFLAMED DERMIS
Inflamed tissue and poor blood flow reduce nutrient delivery to follicles.
2. SUDDEN HAIR LOSS
POOR CIRCULATION
Reduced flow limits nutrients reaching bulbs, triggering shedding.
NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCY
Lack of nutrients and trace elements forces early entry into telogen phase.
WHY DOES IT HAPPEN?
1. GRADUAL HAIR LOSS
VASCULAR: poor blood flow to bulbs.
HORMONAL: excess sebum suffocates hair.
TISSULAR: rigid, irritated tissue shortens hair life.
To slow gradual loss, treat all three causes together.
2. SUDDEN HAIR LOSS
Usually triggered by a specific event within 2-3 months:
- Seasonal changes
- Stress / emotional shock
- Poor diet
- Fatigue / illness
- Certain treatments or chemotherapy
Hormonal shifts after pregnancy also cause temporary shedding.
OUR METHOD TO CURE HAIR LOSS
René Furterer developed 4 key steps to treat hair loss effectively.